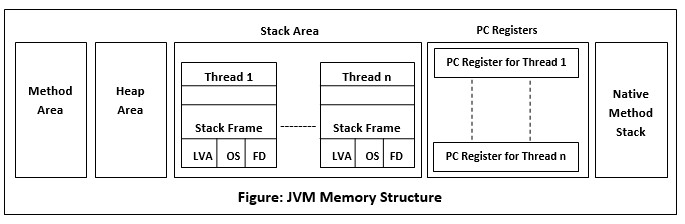

Java memory management JVM manages memory without having user to explictly manage memory by using something called as Garbage Collector. Garbage collection is a process of reclaiming the runtime unused memory automatically. In other words, it is a way to destroy the unused objects. JVM divides memory into 3 parts
static keyword. Stringpool was also a part of this space till java 7 but was moved out
as the space in here is limited.
Apart from the above stuff this space also stored JIT Information, bytecode.
Due to limited space in PermGen Out of memory error was pretty common in Java 7 and
below. In Java 8 PermGen was removed and replaced with Metaspace which is
a part of Heap memory.
Since Metaspace is part of Heap its garbage collected in an even better manner and can
automatically scale based on the need which was not possible with PermGen.metaspace and heap by using the following
parameters. Note that Metaspace parameters only work with java 8 and above and PermGen
parameters only work with java 7 and below.PermGen parameters -XX:PermSize=200m sets PermGen
size to 200MB and -XX:MaxPermSize=300m sets max PermGen size to
300MB.Metaspace parameters are as followsMetaspaceSize and MaxMetaspaceSize – we can set the
Metaspace upper bounds.MinMetaspaceFreeRatio – is the minimum percentage of class metadata
capacity free after garbage collectionMaxMetaspaceFreeRatio – is the maximum percentage of class metadata
capacity free after a garbage collection to avoid a reduction in the amount of space
Garbage Collection in Oracle's HotSpot JVM works using Mark Sweep algorithm which works as follows. Reference
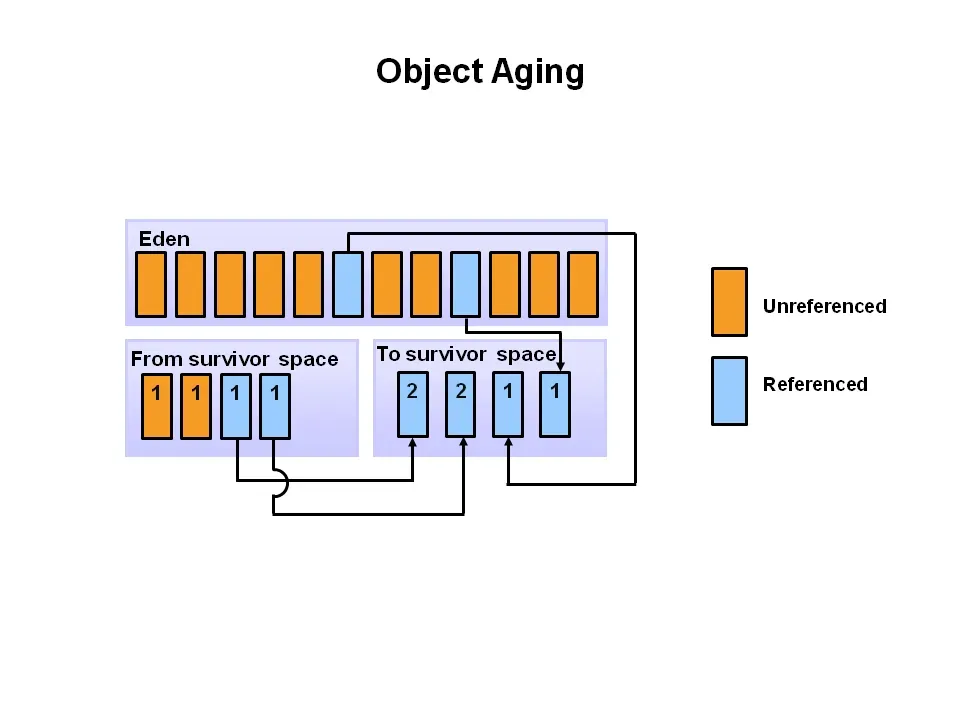
Before we understand the garbage collection process let's see different sections of the heap.
First when a new object is created its is stored in eden space, when garbage
collector starts its minor cycle it marks all objects which are unrefrenced in
young generation. Then eden space that are unreferenced are cleared and the objects
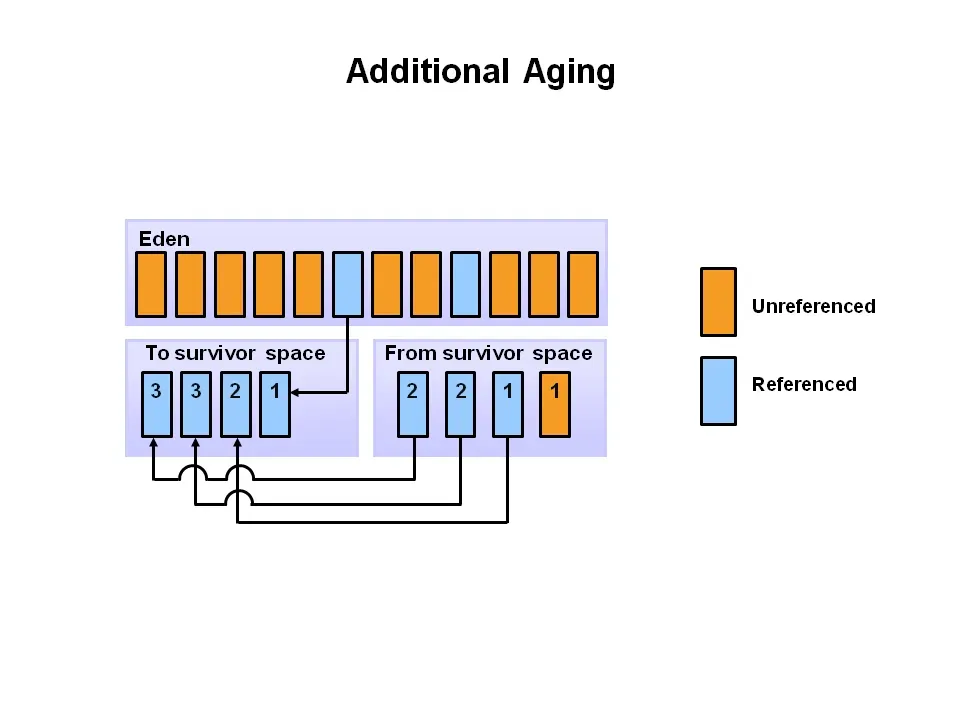
that have references are moved to S0. In the next minor cycle unreferenced objects
are cleared asusual but all referenced objects in S0 and Eden space
are moved to S1. In the next cycle all unreferenced objects are cleared but the
ones holding references are moved from S1 and eden space to
S0. Also as this process keeps happening objects that survive have a counter
attached which tracks how many cycles the object has survived.
Once the counter reaches a certain threshold the object is moved from young generation to old generation or Tenured Generation.
Major cycle cleans up the tenured generation but it is less frequent as it is slow and involves a lot of long lived objects which probably don't need cleaning as they are still being used so a lot of work is wasted, this allows us to keep minor cycles faster as it tracks fewer number of objects
Keeping GC cycles fast is important as GC is stop of the world as in application pauses when GC is running to ensure memory integrity intact.
Now that we understand how GC works let's formally see what's mark and sweep algorithm and different steps involved in it

There are 4 types of Garbage Collectors in HotSpot JVM
-client option.-server
option.-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC. Reference
APIs are used to expose functionality of an application to other applications or users. For example, if you want to use google maps in your application you can use google maps API to do so. Similarly if you want to use facebook login in your application you can use facebook login API to do so.
HTTP Structure -- There are 2 main parts of using HTTP, one we make a request to fetch/modify a HTTP resource then the server responds with a response.
REQUEST
HEADERS
BODY
RESPONSE
HEADERS
BODY -JSON =? REST / XML =>SOAP
GET -> GET/READ
POSt -> UPDATE/SEND
PUT -> CREATE
DELETE -> DELETE
HTTP
2XX - SUCCESS
3XX - REDIRECT
4XX - USER ERROR
5XX - SERVER ERROR
PermGen -- This is a special memory area separated from main heap area
and stores metadata about classes, methods and static items i.e anything defined with the
static keyword. Stringpool was also a part of this space till java 7 but was moved out as the
space in here is limited.
Apart from the above stuff this space also stored JIT Information, bytecode.
Due to limited space in PermGen Out of memory error was pretty common in Java 7 and below. In
Java 8 PermGen was removed and replaced with Metaspace which is a part of Heap
memory.
Since Metaspace is part of Heap its garbage collected in an even better manner and can
automatically scale based on the need which was not possible with PermGen.PermGen parameters -XX:PermSize=200m sets PermGen
size to 200MB and -XX:MaxPermSize=300m sets max PermGen size to
300MB.Metaspace parameters are as followsMetaspaceSize and MaxMetaspaceSize – we can set the
Metaspace upper bounds.MinMetaspaceFreeRatio – is the minimum percentage of class metadata
capacity free after garbage collectionMaxMetaspaceFreeRatio – is the maximum percentage of class metadata
capacity free after a garbage collection to avoid a reduction in the amount of space
-client option.-server option.-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC. Reference