Intention behind creating java was to create a language that can run anywhere and everywhere. That's why you see the oracle's message that java runs on 1B Devices So they were quite successful in doing that.
Java is actually a language specification, and there are multiple implementations of it
- OpenJDK JVM => Hotspot
- Oracle JVM => RockIt
Java(1995) is a much younger language than python(1991) then the natural question is why is python more feature rich and has more libraries than java. Now that's a quiz question for tomorrow
Java is
- Simple -- Similar syntax as C, so its easier to learn for people coming from C
- Object-Oriented -- Since realworld has a lot of objects, thinking in terms of objects is easier so Java uses Object oriented convention [read-more](OOPS Concepts)
- Portable -- Since JDK compiles
.javafiles to.classfile and.classfile is executable prettymuch anywhere a JVM can run it's portable - Platform independent -- Unlike C/C++ where code has to be compiled seperately for
each environment (OS+CPU Architecture) in Java we only compile once and the
.classfiles will be executable anywhere - Secured -- Java doesn't have explict pointers, each program runs inside JVM
sandbox, classloader in java keeps local
.javafiles and external libraries seperate adding an additional layer of security, Bytecode verifier checks if there's any invalid code or malicious code even before executing the code and secuirty manager monitors each class for things like disk read or write. - Robust -- Has Strong memory management with a garbage collector, avoids security issues due to lack of pointers, has exception handling
- Architecture neutral -- In java datatypes are platform independent and occupy exactly the same space as defined in spec. In C programming, int data type occupies 2 bytes of memory for 32-bit architecture and 4 bytes of memory for 64-bit architecture. However, it occupies 4 bytes of memory for both 32 and 64-bit architectures in Java.
- Interpreted -- Javac creates
.classfile which is executed by JVM making the language interpreted - High Performance -- Even though java is intrepreted which adds a additional layer of translation before the code is executed, java uses JIT compiler to optimize pieces of code that matters making it more performant
- Multithreaded -- Java is multithreaded
- Distributed -- Java allow to create distributed applications which can connect with eachother over a network to execute a task
- Dynamic -- Java is dynamic because classes are loaded on demand as and when they are needed.
How Java works
[.java file] -- Compiler (javac) -> [.class file] -- JVM -> Output
How JVM works
[.class files] -- [Class Loader] -> [Byte code verifier] -> [Intrepreter] -> [Runtime] -> Hardware -> Output
JVM Architecture
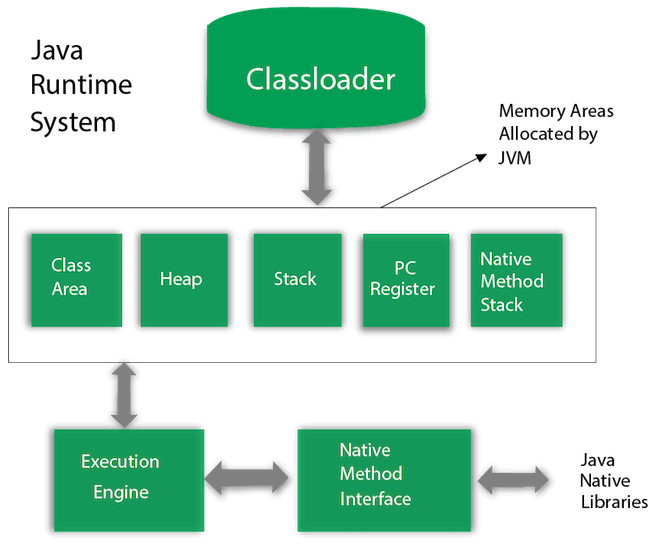
- ClassLoader
- BootStrap class loader -- Loads rt.jar which contains all standard library classes
- Extension class loader -- is a child class of bootstrap class loader and
loads classes in
$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/ext - System class loader -- loads all files in classpath, which is set by
passing
-cpor-classpathargument tojavacommand when executing a class
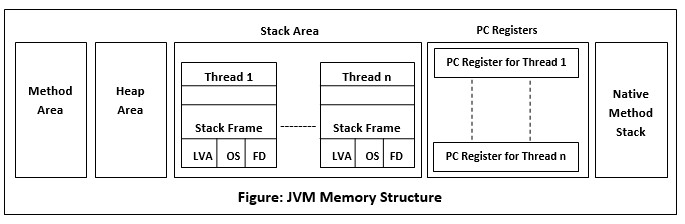
- *Class Area -- Class definations are stored here, this is used to create new classes.
- *Heap -- When an Object instance is created from a class by using
newkeyword it is stored in heap. Note that this heap has nothing to do with datastructure min/max heap even though it has the same name. - *Stack -- Functions as they are executed their local variables are stored here, each thread gets its own stack. Note that this is actually a stack datastructure as i can keep adding new entries to stack as i execute a new function and pop it out as i am done with it. Recurse a lot and you get stackoverflow. Now you know why its called so :P
- PC Register -- Stores the memory Address / location of current instruction being
executed in JVM, it is
undefinedin case of native method - Native method stack -- Java supports running methods/functions written in other languages to be executed in java by using something known as JNI (java native interface) their local
What's a Path Path is a variable that helps OS find where an executable is. This helps us run the executable in terminal, without having to remember the whole file path for that executable.
Type of variables
- Local -- Scoped local to the function being executed. aka only the function being executed can access it.
- Instance -- Scoped at an instance level, aka only the specific instance can access it.
- Static -- Scoped at a class level, aka doesn't need an object instance to be executed and all instances of the class can use it.
Data types
- Primitive
boolean-- 1 bytebyte-- 1 byteschar-- 2 bytes -- java uses 2 bytes incharbecause it uses unicode system not ASCII.short-- 2 bytesint-- 4 bytes - integer literals areintby defaultlong-- 8 bytesfloat-- 4 bytesdouble-- 8 bytes -- decimal literals aredoubleby default
- Non Primitive -- Any Object instance / array is a non primitive type
Operators
-
Operator Type Category Precedence Unary postfix expr++ expr-- prefix ++expr --expr +expr -expr ~ ! Arithmetic multiplicative * / % additive + - Shift shift << >> >>> Relational comparison < > <= >= instanceof equality == != Bitwise bitwise AND & bitwise exclusive OR ^ bitwise inclusive OR | Logical logical AND && logical OR || Ternary ternary ? : Assignment assignment = += -= *= /= %= &= ^=
Important Keywords when coming from C
class-- Javaclasskeyword is used to declare a class.implements-- Javaimplementskeyword is used to implement an interface.instanceof-- Javainstanceofkeyword is used to test whether the object is an instance of the specified class or implements an interface.interface-- Javainterfacekeyword is used to declare an interface. It can have only abstract methods.native-- Javanativekeyword is used to specify that a method is implemented in native code using JNI (Java Native Interface).new-- Javanewkeyword is used to create new objects.null-- Javanullkeyword is used to indicate that a reference does not refer to anything. It removes the garbage value.package-- Javapackagekeyword is used to declare a Java package that includes the classes.strictfp-- Javastrictfpis used to restrict the floating-point calculations to ensure portability.synchronized-- Javasynchronizedkeyword is used to specify the critical sections or methods in multithreaded code.this-- Javathiskeyword can be used to refer the current object in a method or constructor.throw-- The Javathrowkeyword is used to explicitly throw an exception. Thethrowkeyword is mainly used to throw custom exceptions. It is followed by an instance.throws-- The Javathrowskeyword is used to declare an exception. Checked exceptions can be propagated with throws.try-- Javatrykeyword is used to start a block of code that will be tested for exceptions. The try block must be followed by eithercatchorfinallyblock.catch-- Javacatchkeyword is used to catch the exceptions generated bytrystatements. It must be used after thetryblock only.finally-- Javafinallykeyword indicates a block of code in atry-catchstructure. This block is always executed whether an exception is handled or not.super-- Javasuperkeyword is a reference variable that is used to refer to parent class objects. It can be used to invoke the immediate parent class method.